Introduction to Arduino Bluetooth Home Automation
Welcome to CircuitOfThings — your hub for DIY electronics! ⚡
In this guide, you’ll build a powerful Arduino Bluetooth Home Automation system that lets you control two electrical appliances directly from your smartphone using the KSP Bluetooth Control App.
Your Arduino UNO communicates with the HC-05 Bluetooth module and manages two appliances through a 2-channel relay module, while an I2C LCD displays the ON/OFF status in real time.
Why Choose Arduino Bluetooth Home Automation?
This project is perfect for learning embedded control and mobile app integration.
You’ll understand how to use Bluetooth serial communication, relay switching, and I2C LCD display updates — all in one compact, low-cost smart home setup.
Advantages:
- Safe and reliable switching
- Wireless control with instant response
- No Wi-Fi or internet needed
- Expandable to 4–8 devices
Components Required
| Component | Quantity | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Arduino UNO | 1 | The main controller board |
| HC-05 Bluetooth Module | 1 | Enables wireless communication |
| 2-Channel Relay Module | 1 | Controls two AC/DC appliances |
| I2C 16×2 LCD (Address: 0x27) | 1 | Displays relay statuses |
| Jumper Wires | As required | For interconnections |
| USB Cable | 1 | For programming the Arduino |
| KSP Bluetooth Control App | 1 | Android app to control via Bluetooth |
Circuit Connections
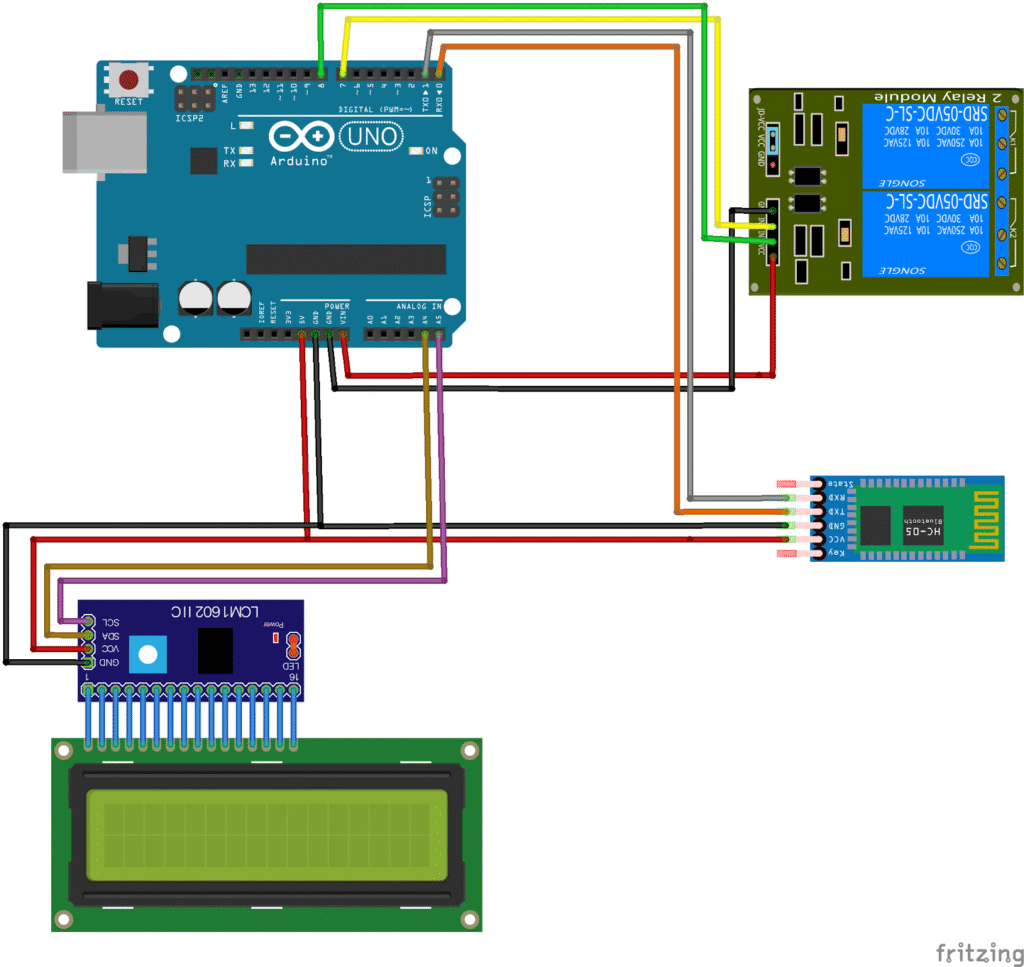
| Component | Pin | Arduino Pin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Relay Module | IN1 | D7 | Relay 1 control |
| Relay Module | IN2 | D8 | Relay 2 control |
| Relay Module | VCC | 5V | Power supply |
| Relay Module | GND | GND | Common ground |
| HC-05 Bluetooth | VCC | 5V | Power supply |
| HC-05 Bluetooth | GND | GND | Common ground |
| HC-05 Bluetooth | TXD | RX (D0) | Serial receive |
| HC-05 Bluetooth | RXD | TX (D1 via divider) | Use voltage divider |
| I2C LCD | SDA | A4 | Data line |
| I2C LCD | SCL | A5 | Clock line |
| I2C LCD | VCC | 5V | Power |
| I2C LCD | GND | GND | Common ground |
💡 Tip: Always use a voltage divider between Arduino TX (5V) and HC-05 RX (3.3V) to avoid damage.
Programming the Arduino
Upload the following code to your Arduino Uno:
#include <Wire.h>
#include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h>
LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x27, 16, 2);
const int relay1Pin = 7;
const int relay2Pin = 8;
String inputCommand = "";
void setup() {
pinMode(relay1Pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(relay2Pin, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(relay1Pin, LOW);
digitalWrite(relay2Pin, LOW);
lcd.init();
lcd.backlight();
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("Relay1: OFF");
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print("Relay2: OFF");
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
if (Serial.available()) {
char c = Serial.read();
if (c == '\n' || c == '\r') {
inputCommand.trim();
handleCommand(inputCommand);
inputCommand = "";
} else {
inputCommand += c;
}
}
}
void handleCommand(String cmd) {
if (cmd == "ON1") {
digitalWrite(relay1Pin, HIGH);
updateLCD(1, true);
} else if (cmd == "OFF1") {
digitalWrite(relay1Pin, LOW);
updateLCD(1, false);
} else if (cmd == "ON2") {
digitalWrite(relay2Pin, HIGH);
updateLCD(2, true);
} else if (cmd == "OFF2") {
digitalWrite(relay2Pin, LOW);
updateLCD(2, false);
}
}
void updateLCD(int relayNum, bool state) {
if (relayNum == 1) {
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("Relay1: ");
lcd.print(state ? "ON " : "OFF");
} else if (relayNum == 2) {
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print("Relay2: ");
lcd.print(state ? "ON " : "OFF");
}
}
Controlling via KSP Bluetooth Control App
To make the project interactive, we’ll use the official KSP Bluetooth Control App developed by KSP Electronics.
Download the App:
📱 KSP Bluetooth Control on Google Play
App Setup Steps:
- Open the KSP Bluetooth Control App on your Android phone.
- Pair your HC-05 module (default PIN:
1234or0000). - Tap “Connect Device” and select your HC-05 from the list.
- Create two control buttons:
- Button 1:
- Name: Relay 1 ON
- Command:
ON1
- Button 2:
- Name: Relay 1 OFF
- Command:
OFF1
- Button 3:
- Name: Relay 2 ON
- Command:
ON2
- Button 4:
- Name: Relay 2 OFF
- Command:
OFF2
- Button 1:
- Press the respective buttons — the connected relays will toggle, and the LCD will display real-time status for both relays.
✅ Pro Tip: You can also customize button colors, icons, and command feedback text within the app.
LCD Display Output
The LCD displays the live relay status:
Relay1: ON
Relay2: OFF
Whenever you send a command through the KSP Bluetooth app, the display updates immediately.
Safety Precautions
⚠️ Important Notes:
- Never touch relay terminals when connected to AC voltage.
- Always use opto-isolated relays for mains appliances.
- Keep high-voltage wiring separate from your Arduino circuit.
- Double-check all connections before powering the system.
- Use an insulated enclosure to prevent accidental contact.
Learning Outcomes
By completing this project, you’ll understand:
- How to use Bluetooth serial communication with Arduino.
- How to control relays using digital pins.
- How to display real-time system data using an I2C LCD.
- How to integrate smartphone-based control into embedded systems.
Project Extensions
- Add more relays for additional appliances.
- Replace HC-05 with ESP32 for Wi-Fi control.
- Add sensors (temperature, motion, etc.) for automation.
- Use voice commands through a custom Android app.
- Create a dashboard UI in MIT App Inventor.
Read More:
- ESP8266-01 Pinout: A Comprehensive Guide to Pin Configuration
- Raspberry Pi: How to Control a DC Motor with L298N and PWN on a Web Server
Conclusion
This project is a great hands-on introduction to Bluetooth-based home automation using Arduino.
With the KSP Bluetooth Control app, you can enjoy a professional, responsive interface to control your devices and visualize their status instantly.
You now have the foundation to expand your system into a full-fledged smart home project!